Rainwater Harvesting: Road to water security and self-reliance

India is blessed with 2 monsoons. The average annual rainfall for India would be around 117-125 cms. Many parts of India get sufficient rains, which would be sufficient for our use in our cities, towns, and villages if harnessed properly. But we let most of this water go into the drains, especially in urban areas, which causes urban flooding. On the other hand, we suffer from water shortages, especially in the summer months. Rainwater harvesting is one easy solution to augment our water security.
At a broad level, we need the following 3 things for rainwater harvesting
- A catchment area or collection area over which rain falls to collect the rainfall.
- Appropriate storage to store the water falling onto the catchment area.
- A channel to transfer the water collected in the catchment or collection area to the storage.
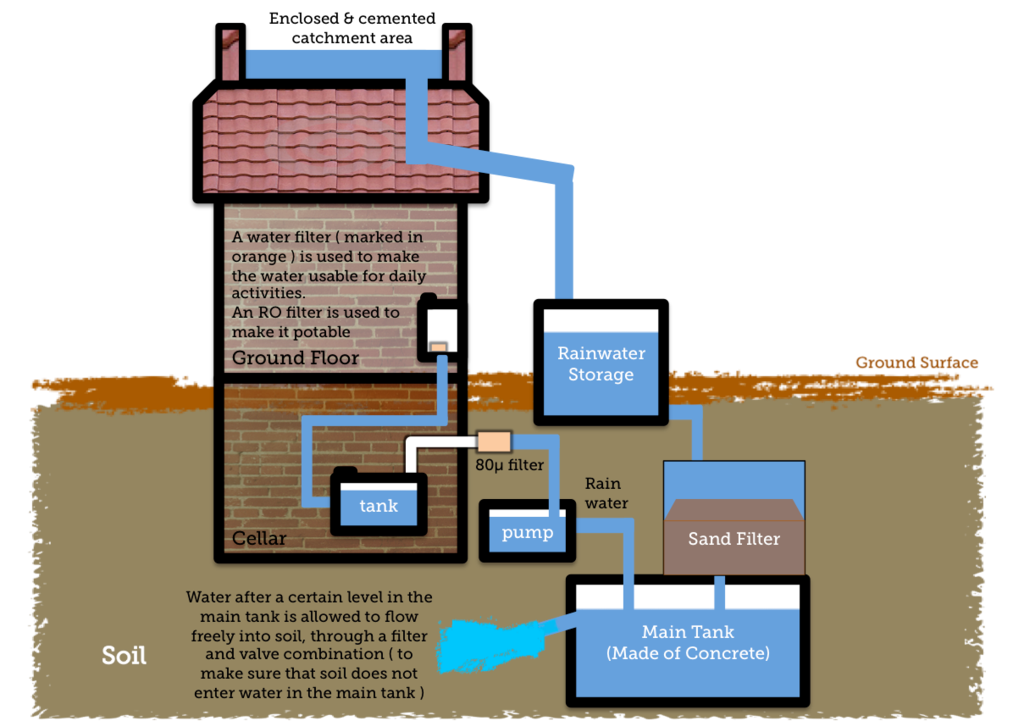
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting (RWH)
A typical 100 sq.m roof would collect around 100 cm of rain (assuming 117 cms of average rainfall with 80-85% collection efficiency). You potentially harvest 100*100/100 cubic meters = 100 Kilolitres of rainwater. The typical daily need is around 135 liters/person. The water captured from 100 sq.m can support the needs of 2 people for the full year.
- Ensure that the roof surface is cleaned of debris before each monsoon season.
- If you have a flat roof, it typically has a slope. Usually, a rainwater outlet is provided at the sloping end of the roof which connects to a vertical drain pipe to drain rainwater from the roof.
- Ensure a grill is installed at the rainwater outlet pipe in the terrace to catch any leaves or other debris. Ensure that grill is kept clear at all times.
- If you have a sloping roof, ensure that a gutter is installed to catch the rainwater at the edge of the roof. A vertical drain pipe should be installed at the end of the gutter to drain the water.
- Have a provision to flush the first ten minutes of rain using a bypass arrangement before collecting and channeling the remaining rainwater.
- Channel the rainwater collected from the roof through the vertical drainpipe to an above-ground tank or an underground sump and store it for future use. The overflow can be channeled to recharge the groundwater.
- Alternatively, the rainwater collected from the roof can be channeled directly to recharge the groundwater through a recharge pit or dug wells or tube wells, or inverse borewell.
Surface Runoff Rainwater Harvesting (RWH)
The rainwater falling on the open areas around the house like compound area, garden, pathways, driveways, parking lot, etc is known as surface runoff. This surface run-off typically flows into the stormwater drains or sewage drains or onto the roads. If there are excess rains or blocked drains it leads to urban flooding.
The surface run-offs around a house or apartment or gated community can be channeled through stormwater drains into the ground through recharge pits or tube wells or inverse borewells.
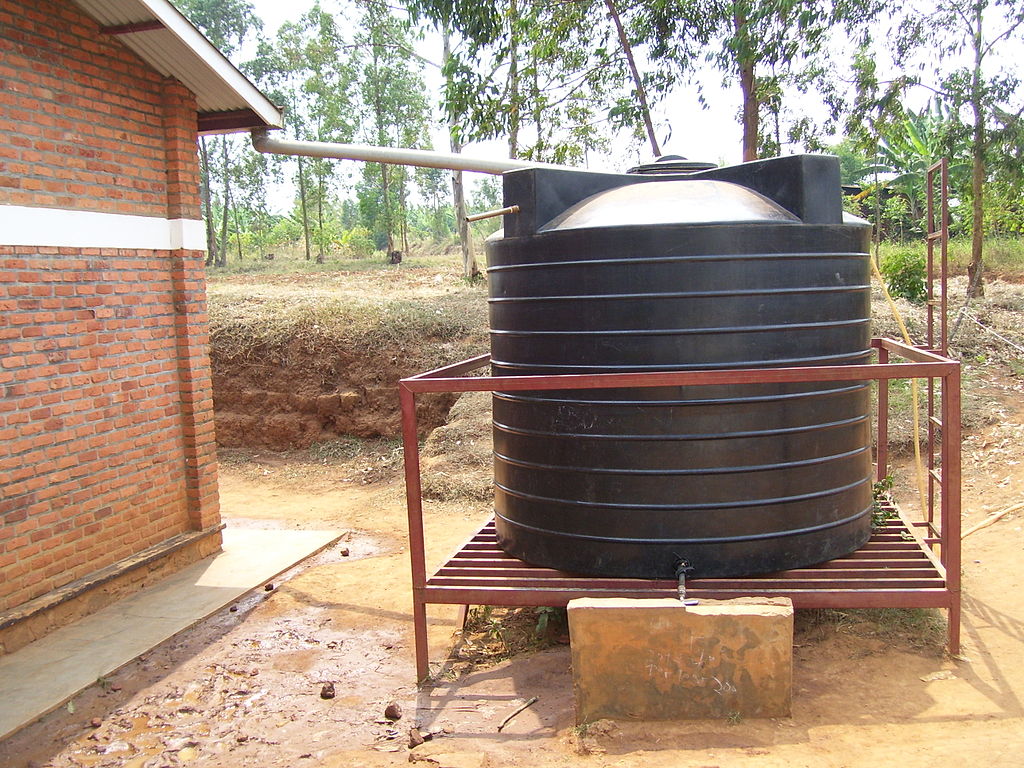
Rainwater Harvesting(RWH) into Storage sumps
You can use an above-ground storage tank or underground storage sump to store the rainwater collected on the roof. The challenge would be to get a tank or sump with enough storage capacity to store the entire water collected. But you can store drinking water supply sufficient for a year in a tank or a sump. This would be helpful especially if the groundwater is hard or you have challenges in getting a clean drinking water supply. A typical household of 4 would need about 25-30 litres of water for drinking and cooking per day. The capacity of the tank or the sump required can be calculated accordingly. The excess water can be channeled into the ground for recharge. The water stored in the tank or the sump can be used for drinking and cooking through an outlet in the kitchen.

Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) into Recharge Pits
A recharge pit is a simple way to channel water from roof and surface runoff into the ground. You can have one or multiple pits depending on the area and collection points.
The pit should be deep enough to penetrate through the imperious layers. You can add a simple multilayer filtration system consisting of pebbles, gravel, and sand to filter the impurities with water. You can also add a layer of carbon bed filter, in the form of a charcoal bed or activated charcoal bed. Ensure that the recharge pit is clear of all debris before the rainy season begins.
Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) into dug wells
If you have space a covered dug well is ideal for rainwater harvesting. If there are defunct dug wells around the area, see if they can be revived after doing necessary repairs. The rainwater can be channeled from the recharge pit after filtration, through pipes into the dug well. The rainwater collected from the roof can also be directly channeled into the dug well.
Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) through Inverse BoreWell (IBW)
An unused or defunct borewell can be used to recharge groundwater. This can be achieved by creating a recharge pit around the mouth of the borewell. The first few feet of the borewell tube can be replaced with plastic or metal tube with openings and mesh. This would allow the water to seep into the ground through the borewell.
Alternatively, water from the recharge pit after filtration can be channeled through pipes and connected into the borewell tube.
Additional Resources on Rainwater Harvesting
- Self-reliance in water: A book by Indukanth Ragade is an excellent practitioner’s guide to rainwater harvesting, water conservation, water recycling, and self-reliance in water.
- Centre for Science & Environment(CSE)’s has been promoting the concept of rainwater harvesting in India. Its portal http://www.rainwaterharvesting.org/ has a comprehensive repository and database on rainwater harvesting resources and projects.
- Akash Ganga Trust runs a free Rain Centre in Chennai which is a model house on RWH and also a place to learn about various designs, cost estimates, and a list of contractors to implement RWH in independent houses, flat complexes, offices, factories, Institutions, etc.
- HMWSSB has a Rainwater Harvesting Theme Park in Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad consisting of more than 40 interventions on the theme of Water conservation, Rainwater Harvesting, Groundwater recharge, Water treatment, and Sewerage treatment.
- KSCST with the support of BWSSB has established RWH Helpdesk at KSCST in Indian Institute of Science campus and also Sir. M. Visvesvaraya Rainwater Harvesting theme park in Jayanagar Bangalore.
Water can be recycled for use within homes, communities, and establishments. Learn more about water recycling to save water and reduce your water bill.



Responses